
Chapter 2: Brain State Model
 Executive Skills: A TOP WIFE Makes Good TEa
Executive Skills: A TOP WIFE Makes Good TEa
Attention: The ability to sustain attention in spite of distractibility, boredom or fatigue.
Time Management: The capacity to estimate how much time one has, how to allocate it, and how to stay within time limits and deadlines. A sense that time is important.
Organization: The ability to create and maintain systems to keep track of information or materials.
Prioritization: The ability to see what is most important and make a plan to accomplish it.
Working Memory: The ability to hold information in memory while performing complex tasks, and the ability to draw on past learning or experiences to apply to the situation at hand or project into the future.
Impulse Control: The capacity to think before you act, allowing you to evaluate a situation and how your behavior might impact it.
Flexibility: The ability to revise plans in the face of obstacles, setbacks, new information or mistakes. Adapting to changing conditions.
Empathy: Understand what others feel and see from another’s point of view.
Metacognition: The ability to step back and take a bird’s eye view of yourself in a situation. To observe yourself (reflect and witness), self-monitor and self-evaluate.
Goal Achievement: The capacity to set a goal and follow through to completion.
Task Initiation: The ability to begin projects without undue procrastination, in an efficient and timely fashion.
Emotional Control: The ability to manage emotions.
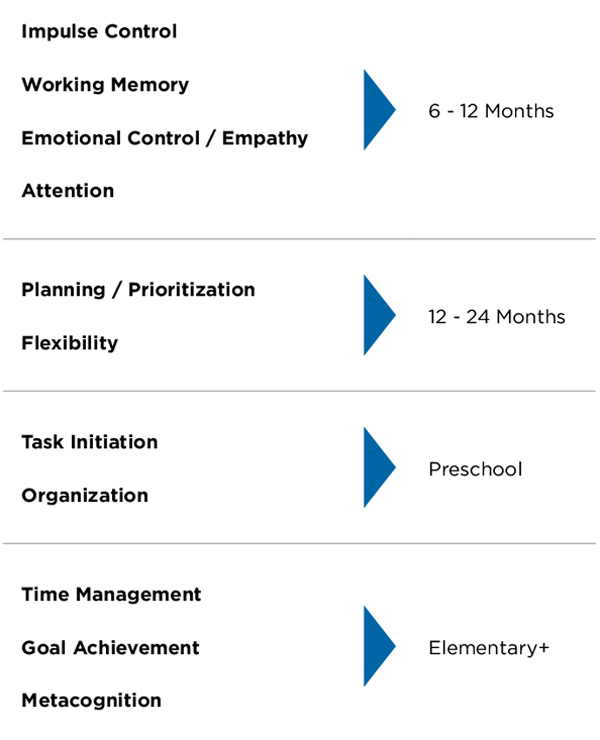
 Developmental Order of Executive Skills
Developmental Order of Executive Skills
The following chart shows the approximate times when different executive skills begin their developmental journey.
 A Grandmother’s Success Story
A Grandmother’s Success Story


 How to Represent the Brain with Your Hand
How to Represent the Brain with Your Hand


